1. Disease causes
An acute infectious disease caused by the bacteria Pasteurella multocida of the Pasteurellaceae family
2. Disease epidemiology
The disease is endemic and occurs worldwide
The disease is common in countries with tropical climates, including Vietnam
The disease occurs in ducks and geese of all ages, when stressed or during seasonal changes, the disease progresses rapidly and causes a high mortality rate
The disease occurs due to the following causes:
Infectious objects transmitted to other birds
Waste from sick poultry, water washed when slaughtering dead poultry
The disease occurs spontaneously: healthy poultry already carry the pathogen, when resistance decreases, the pathogen can increase its virulence and cause disease
Poor farming conditions, poor hygiene, poor control of flock entry ... are also factors that spread the pathogen
3. Disease symptoms
Depending on the virulence of the pathogen:
Hyper-acute form: causes rapid death, no symptoms can be observed.
Healthy ducks suddenly become depressed, have high fever, and die after 1-2 hours. The mortality rate can be up to 50%
Laying ducks often have broken eggs and die

- Acute form:
Ducks are lethargic, wobbly, stop eating, have ruffled feathers, walk slowly or have paralyzed legs; nose and mouth discharge mucus, foam mixed with dark red blood
Duck has diarrhea, loose stools are black-gray, green or yellow,
Duck has fever of 43 - 44⁰C, thirsty, lies flat
Facial hematoma (no neurological symptoms)
Ducks usually die after 2 - 5 days, the mortality rate is often high at night.
In laying ducks, young eggs are deformed, broken
- Chronic form: Ducks and geese show signs of emaciation, skin and bones due to the disease affecting many internal organs. The thigh, knee and ankle joints are chronically inflamed, sometimes meningitis and neurological symptoms are seen


4. Lesions
- Acute: hematoma and hemorrhage appear in subcutaneous connective tissue, sinuses and organs in the body; pulmonary hematoma.
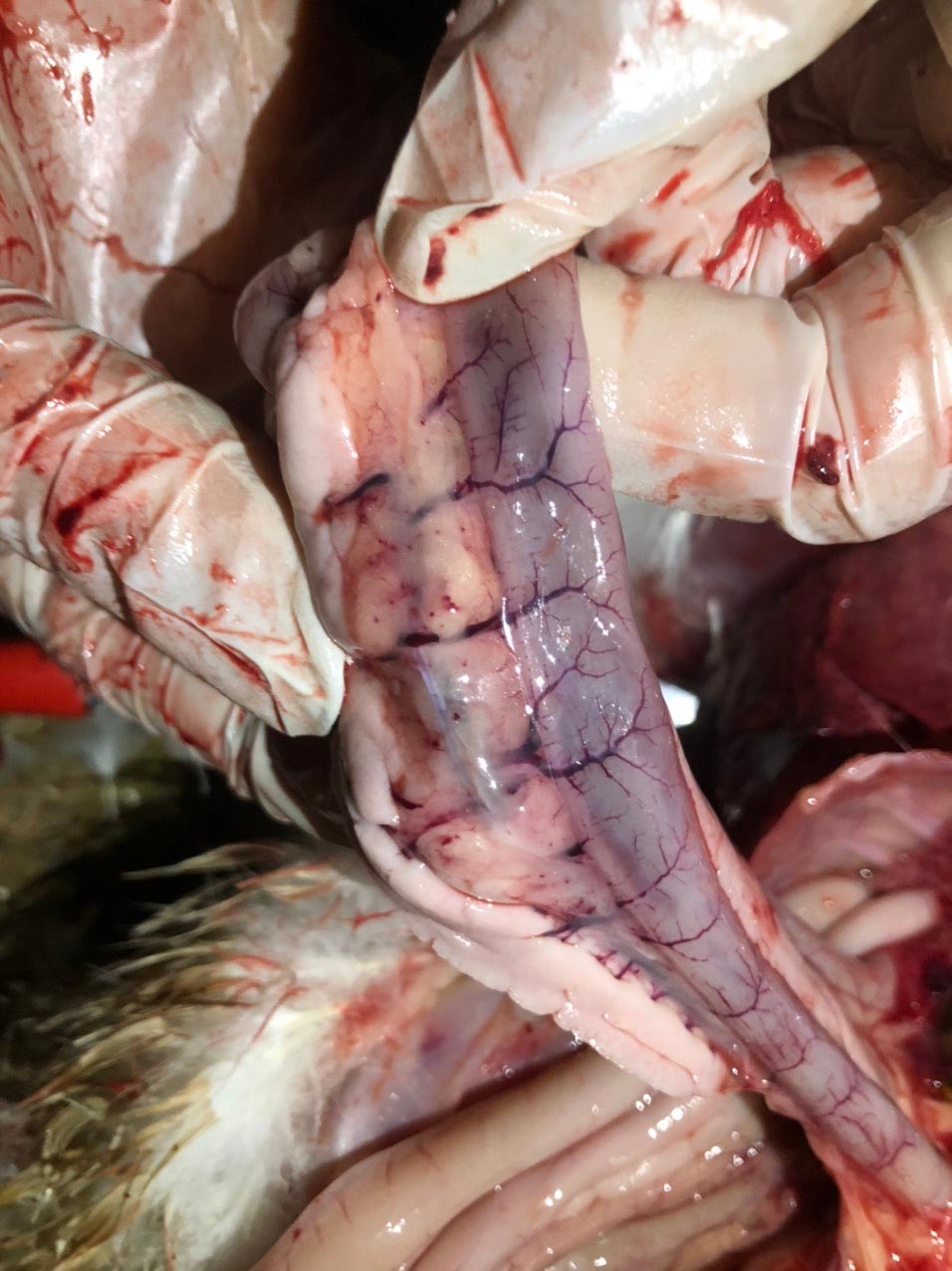

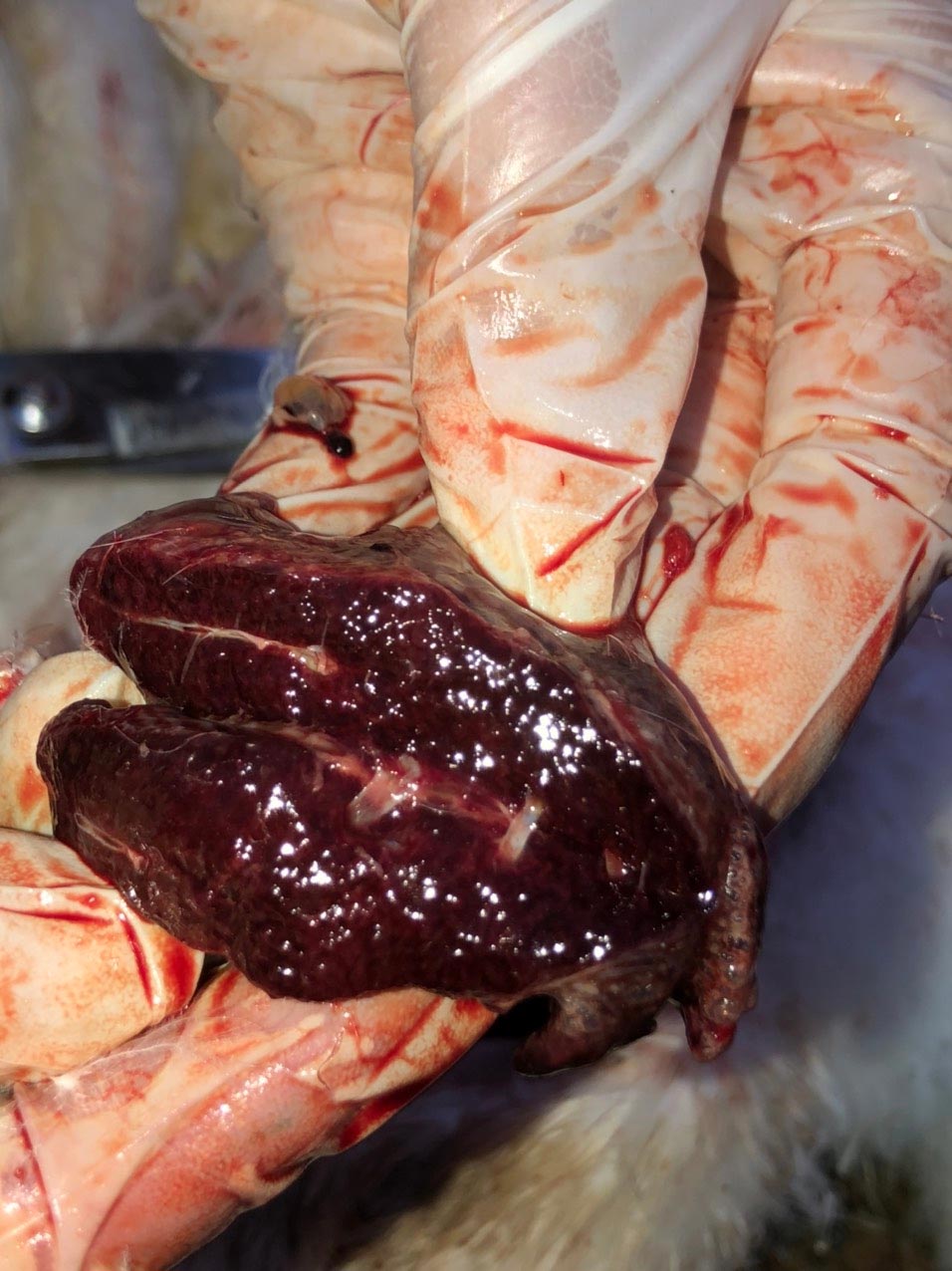
- Chronic cases:
The pericardium, liver membrane, and air sacs are severely inflamed and tough, difficult to cut
A white layer of bean curd covers the entire front of the lungs, and the eye sinuses also have white bean curd
The ovaries and fallopian tubes are inflamed, swollen, pale yellow, and filled with water
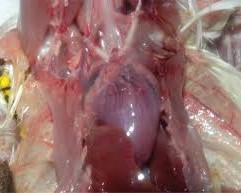
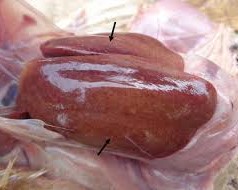
5. Diagnosis
- Diagnosis is mainly based on clinical symptoms and typical surgical lesions of THT
- Differential diagnosis with Avian influenza, typhoid, etc.
6. Disease prevention
- Raise ducks and geese at appropriate density
- Keep barns clean and airy in summer, warm in winter
- Implement control of flock entry, ensure barns are isolated for at least 2 weeks between 2 consecutive batches
- Spray DONACID or DOCIDINE disinfectant periodically 1-2 times/week in barns and surrounding areas


- Enhance resistance, prevent stress when weather changes, move poultry cages with products: VP1000, HEPAMITOL, GREENBIOLAC, VITA C 15% ...



- When the weather changes, it is necessary to prevent antibiotics for the whole herd with AMOX - COLIS or DONA ENRO 20.


7. Treatment
- The whole herd uses AMOXY - 500 or DONA ENRO 200 or FLODOXY mixed with bran or dissolved in drinking water according to the treatment dose


- Use ELECTROLYTE, PARA – C, HEPAMITOL, VP1000 to help the flock recover quickly.


- Separate weak ducks and geese into isolation pens and inject them with CEFTIFEN.












